How high are the clouds. How to distinguish between different types of clouds. Where clouds meet
The Sun moves in the constellation of Cancer until August 11, and then in the constellation Leo, at the same time until August 22 it is in the zodiac sign of Leo, and then moves in the sign of Virgo. August 1, 2008 - 2454680 day according to the Julian calendar, the Sun rises at 5:34 am, sets at 21:36 Moscow (summer) time. August 31 - 2454710 Julian day, sunrise at 6:33 and setting at 20:25. Days in the middle of the month are 15 hours and nights are 9 hours. pay attention to the red color of our luminary. If there is still a slight haze, then practically without protective dark glasses you can see how irregular shape Sun, and large spots on it (if they are, of course, these days). The flattened, asymmetrical shape of the solar disk is caused by the phenomenon of refraction in the atmosphere, as a result of which all celestial bodies are perceived somewhat elevated above the horizon - the more, the closer they are to the horizon. The lower edge of the Sun rises more strongly, the upper one less.
There will be two eclipses this month: on August 1, during the new moon, a total solar eclipse visible in Western Siberia and the Altai Territory, and on August 17, during the full moon, the Moon will pass through the earth's shadow, and there will be a partial lunar eclipse, visible throughout Russia.
Circumstances of a total solar eclipse in the band of the total phase of the eclipse

Total solar eclipse on August 1, 2008 belongs to the 126th series of saros according to the international classification. The positions of the Moon and the Sun in relation to the Earth are repeated with high accuracy through saros- a period of 18 years and 11.3 days (or 18 years and 10.3 days, if five leap years fit into this period). The previous total solar eclipse occurred on July 22, 1990. Interestingly, after 54 years and 34 days, i.e. after three saros, the lunar shadow will be approximately in the same place on the surface of the Earth - this is a large saros. It will fall on September 2062, when a total solar eclipse will then be observed in approximately the same places as this year.
During a saros, an average of 70–71 eclipses occur, of which 42–43 are solar (14 total, 13–14 annular, and 15 partial) and 28 lunar. The next total solar eclipse in Moscow will take place on October 16, 2126.
Knowledge of saros made it possible to clarify the chronology of ancient events that occurred during eclipses. So, in Herodotus we read: “The Lydians and the Medes waged war for five years in a row. The war continued with equal success on both sides, but in the sixth year that the troops fought, the day suddenly turned into night. Thales of Miletus predicted this phenomenon to the Ionians, accurately indicating the year when the eclipse was to occur. The Lydians and the Medes, seeing that the night suddenly covered the earth, stopped the battle and began to worry only about how to make peace. This eclipse is known as Eclipse of Thales. Calculations show that the battle between the Lydians and the Medes took place during the eclipse of May 28, 585 BC.
The surviving data on the course of eclipses in ancient times showed that the Earth slows down its rotation. Indeed, knowledge of the saros period makes it possible to accurately calculate when, in what place, and even at what hour the eclipse occurred. But calculations carried out in the 18th century showed a discrepancy between the time of day the beginning of eclipses, which astronomers calculated, and what actually happened. The eclipses began almost 3 hours earlier than the calculations predicted. This discrepancy can be explained if we assume that the duration of the day is lengthening - by about 0.0023 s per 100 years. Why is this happening?
Back in 1754, the German philosopher Immanuel Kant suggested that the tides that the Moon causes on Earth lengthen the duration of the day due to tidal friction between the water shell and the solid surface of the Earth. The deceleration of the Earth's rotation predicted by Kant was actually discovered and measured in the middle of the 20th century. The magnitude of the angular deceleration of rotation, according to modern data, is 4.81 10 -22 radians per second per second (the current value of the angular velocity of the Earth's rotation + =
\u003d 7.292115 10 -5 rad / s), which corresponds to an increase in the length of the day just by these 0.0023 s in 100 years, and in 2000 years - by as much as 3.5 hours.
A total solar eclipse is depicted in a painting by the artist and architect of the first half of the 18th century. Kosmas Damian Asam "Solar eclipse", - he is observed by St. Benedict. Apparently, this is one of the three total solar eclipses that the artist himself observed (1706, 1724 and 1733). The painting is one of the earliest realistic depictions of an eclipse in history. The solar crown and diamond ring are clearly visible - Sun rays, which for fractions of a second make their way through the gorges of the mountains on the edge of the moon. You, too, may be lucky if you carefully follow the course of the eclipse, especially in the last moments before the onset of its full phase. By the way, the eclipse of August 1, 2008 is a continuation through 16 and 15 periods of saros, respectively, of the eclipses of 1706 and 1724. So we have the opportunity to compare the appearance of the solar corona this year with what was observed in those distant years.

Painting "Solar Eclipse" Cosmas Damian Asam(1735), Weltenberg Abbey, Bavaria. http://www.sai.msu.su/apod/image/0801/eclipse_pasachoff_big.jpg
Circumstances of a partial eclipse of the Moon (UT)
Kostroma |
||||
Norilsk |
||||
Orenburg |
||||
Stavropol |
||||
Tolyatti |
||||
Chelyabinsk |
||||
Yaroslavl |
Partial lunar eclipse August 16 is a repetition through the saros of the total eclipse of August 6, 1990, which was observed in the eastern regions of Russia. It will be private with a maximum phase of 0.81 and will be fully visible in the European part of the country, and in Siberia the Moon will set in various phases of the eclipse. No eclipse will be observed in the Far East and Kamchatka. The partial eclipse will last more than 3 hours, and the penumbral phases will last more than an hour. The maximum phase will come at 21:30 UT, when it will already be 1:30 in Moscow summer time. Interestingly, 1.5 hours before the start of the private phase, the Moon will cover Neptune (in the constellation of Capricorn).
Detailed information about eclipses can be found at http://www.astronet.ru/db/msg/1223333.
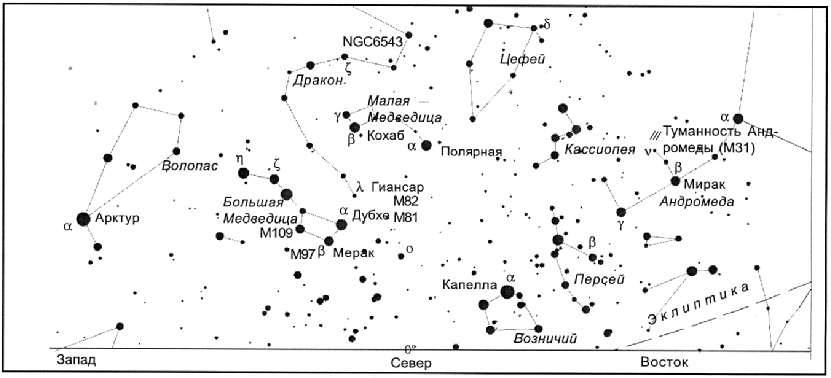
Going outside at about 10 p.m., we will see the same constellations as at midnight in July. First of all, let's pay attention to three bright stars located in the northeast near the zenith, almost overhead at the tops of an almost regular, so-called Summer-Autumn Triangle. These are Vega (Lyra), Deneb (Swan) and Altair (Eagle).

Above all is Deneb, the brightest star in the constellation Cygnus, which is shaped like a cross stretched along the silvery band of the Milky Way. It is not surprising that at the beginning of the 16th century, when attempts were made to eradicate the pagan images of the constellations and replace them with Christian ones, this ancient pagan Swan was replaced by a cross held in her hands by St. Helen, the mother of Emperor Constantine. This emperor, the patron saint of Christianity, according to legend, found a genuine cross on which Jesus Christ was crucified three centuries before his reign.

The constellation Cygnus from As-Sufi's Uranometry, 903-986. (http://www.icoproject.org/img/ss9.jpg)
The Romans, like the Greeks, identified this constellation with a swan, the form of which Jupiter (Zeus) assumed in order to seduce the innocent beauty Leda (Nemesis). Such famous astronomers of antiquity as Hipparchus and Ptolemy called this constellation simply bird - Ornis, and many in those days and more ordinary - chicken. The Arabs called him chicken, and dove. The last name was retained for this constellation throughout the Middle Ages. It is for this reason that the name of the brightest star Deneb is short for Arabic dgeneb-ed-dazha zheh (chicken tail). The Star of Albireo (Swan) is located in the "head" of the Cygnus (or at the base of the Cross). This star of the third magnitude in a small telescope appears to be one of the most beautiful double stars (yellow 3 m and blue 5.3 m).
Near the zenith in the northeast is the constellation Cepheus - a pentagon of relatively bright stars. The most distant star from the pole of this pentagon, Cephei, is a well-known and bright pulsating variable star, whose brightness change is always a pleasure to watch (though not so easy to do).

constellations over southern part horizon (at the latitude of Moscow)
Under the left "wing" of Cygnus is the constellation Lyra with the brightest star of the summer sky Vega. Between the stars and you can try to see the ring-shaped planetary nebula M57 - the last breath of a dying star; glitter nebula 9.3 m .
Under the constellation Cygnus, just to the east of the celestial meridian, the constellation Eagle is located. The eagle is the bird of the god Zeus, a symbol of dominance, glory, victory and triumph. The Arabs named the brightest star in this constellation el-nasr el-tair - flying eagle where it comes from modern name Altair.
A little to the west of the celestial meridian is the constellation Ophiuchus familiar to us, the brightest star of which Ras-Alhague (Ophiuchus) is located next to Ras-Algeti (Hercules). The constellation of Ophiuchus is wrapped around by an extended constellation of the Serpent, in which two parts are distinguished - Head of the Serpent, located to the west of Ophiuchus, and the Tail of the Serpent - to the east of it. Find the constellation Ophiuchus will help two bright stars- Altair (Eagle) and Arcturus (Boötes), - in the middle between which it is located.
Constellations over the northern part of the horizon (at the latitude of Moscow)
In the very west, it is easy to detect the constellation Bootes, next to which the necklace of stars of the constellation Northern Crown is noticeable. The star Arcturus (Boötes) is easy to find on the continuation of the straight line connecting the two extreme stars of the “tail” of Ursa Major.
To the east of the celestial meridian, under the constellation Eagle, at the very horizon in the southeast, one can distinguish the constellation Capricorn, which is better seen in the southern regions of Russia.
A small constellation of Dolphin, consisting of stars fainter than 4 m and located somewhat east of Orel, is clearly distinguishable due to the diamond-shaped arrangement of its four brightest stars (all about 4 m).
The constellations Pegasus and Pisces appear in the east.
Turning to the north, we will see the bright Chapel (Auriga) low above the horizon, a little higher, in the northeast, Perseus begins to rise, who hurries to help the beautiful Andromeda. The elongated chain of bright stars of Andromeda just points to Perseus. The most recognizable and conspicuous constellation in the northeast is Cassiopeia, whose five brightest stars are arranged in a W shape.
To the left of the meridian, in the northwest, the Ursa Major Bucket is noticeable, the two extreme stars of which just point to the Polar Star (Ursa Minor). There are many interesting constellations in the north, but it is better to postpone their study for six months, in February, when they will be highest above the horizon.
Now it is better to study the stars and constellations that are near the zenith. So, the two brightest stars - and Ursa Minor - have about 2 m, – about 3 m, and the rest are weaker 4 m. The star of Ursa Minor is called Kokhab (from the Arabic Kohab al-Shemali - Star of the North).
Along the entire south side, near the horizon, one can trace the ecliptic, which stretches through the constellations of Aquarius and Capricorn in the east, Sagittarius and Scorpio in the south, Libra and Virgo in the southwest.
PLANETS
Venus moves along the constellation Leo next to the Sun, therefore it is also not visible.
Mars moves along the constellation Leo next to the Sun, you can try to see it in the first decade of the month for several minutes immediately after sunset, the brightness of the planet is 1.7 m .
Jupiter moves retrogradely along the constellation Sagittarius, visible in the evening and night hours low above the horizon, its brightness is -2.5 m .
Saturn moves along the constellation Leo near the Sun, therefore it is not visible.
Uranus moving backwards in the constellation Aquarius, its brightness is about 6m, you can try to find it with binoculars at night, but this requires detailed map stars in its vicinity.
Neptune moving backwards in the constellation Capricorn, magnitude 7.8 m, you can try to find it with a telescope, but this requires a detailed star map of its surroundings - up to 8 m .
METEOR
Perseids. The stream is active from July 9 to August 17, maximum on August 12–13 (60 met./h). meteors fast, white color, sometimes mass falls are observed - 6-15 meteors in 2-3 minutes. The radiant is in the constellation Perseus, so it is best observed after midnight. By continuing the visible trail of meteors back, you can determine the position of the radiant - the place where all the meteors seem to come from. True, this month the bright Moon in a phase close to the full moon will interfere with observing these meteors.
The article was prepared with the support of Max Sport. If you have a sports trip ahead of you, and there are no team shirts with player numbers, then the best solution to this problem would be to contact the Max Sport company. On the site located at www.Max-Sport.Ru, you can order T-shirts, as well as use the service of applying numbers to textiles. The company "Max Sport" employs only highly qualified specialists with vast experience in working with clients.
August nights in the sky you can observe the five main constellations of this month. Watching them, it seems that you can look into the very heart of the universe. And all because this five contains an extensive list of the most unusual and amazing objects.
Constellations of the summer sky: June | July | August
South Crown

Opens the five August constellations of the Southern Crown. It is one of the smallest and dimmest constellations in the southern hemisphere. The Southern Crown covers an area of 128 square degrees. And with the naked eye, no more than four dozen stars can be distinguished in its composition.
The South Crown is very similar to its northern neighbor, the North Crown. It also has the shape of an arc or crown. It is better to navigate by the star Kaus Australis - the brightest in Sagittarius. To the southeast of it, the desired crown of stars will be located. In this case, the constellation Scorpio will be to the west, and the Altar and Telesokpus - in the south.
The constellation can be observed in the southern and south central regions Russia. The best time to see Corona is in July.
The brightest in the constellation are two stars: Alpha and Beta. Alpha Southern Corona, or Alfekka Southern, is almost 3 times larger than the Sun and is 125 light years away from Earth. Beta Southern Corona is an orange giant and is much further away - at a distance of 508 light years.
A cloud of cosmic dust has stretched across the constellation, making the Southern Corona even less noticeable. The constellation also includes three nebulae of the beautiful blue color and one globular cluster.
Lyra

This is one of the smallest constellations in the northern hemisphere, which, nevertheless, is known for the fact that it includes one of the brightest stars in our sky - Vega.
Lyra can be observed at any time of the year. And her main star, Vega is visible from anywhere in the world except Antarctica. This constellation is never over the horizon though best time summer is considered to be observed.
You can find Lyra by the Summer-Autumn Triangle, since Vega is one of its peaks. The outlines of the constellation resemble a parallelogram, as if "hung on a hook" of Vega.
Vega is Alpha Lyrae, a zero-magnitude star and the fourth brightest luminary in our sky. This blue giant is twice the size of the Sun. By the way, this is the first star to which the distance was first determined. The calculations were made in 1837 by astronomer V. Struve. And this distance is measured in 27 light years.
Beta Lyra is called Sheliak. It is a binary star system surrounded by a cloud of cosmic dust.
A meteor shower passes through the constellation Lyra, which is called the Lyrids. Its speed is about 10 meteors per hour.
The constellation also includes one of the most famous nebulae - the Ring.
Sagittarius

This is one of the largest constellations in the southern hemisphere, covering an area of 867 square degrees. To see Sagittarius in the clusters of the Milky Way, it is easiest to focus on the neighboring constellation Aquila. The tail of the Eagle will just point us to the desired constellation.
Sagittarius is one of the iconic constellations of our sky. First, here is the center of our galaxy. Secondly, you can immediately observe a supermassive black hole. Thirdly, Alpha Sagittarius, the star Kaus-Australis is considered to be navigational. And fourthly, it is here that the most beautiful part of the Milky Way is located.
It is difficult to say what exactly the constellation resembles in outline, since over 200 stars can be distinguished with the naked eye.
The constellation also includes three planetary nebulae at once: Omega, Triple and Lagoon. There are globular clusters here.
Three more interesting facts about this constellation:
An irregular galaxy is located in the northeastern part, and a planet was discovered nearby in 2002.
The star Sagittarius Ross 154 is one of the closest stars to the Sun. The distance to it is only 9.6 light years.
The constellation, plus everything else, also leads in the number of variable stars. There are 5559 of them in its composition.
Shield

The constellation Scutum belongs to the constellation of the southern hemisphere and is located very close to the equator. This is one of the smallest constellations in terms of area, covering an area of only 109 square degrees. In such a site, however, one can distinguish about two dozen stars belonging to the Shield.
You can observe it throughout Russia, south of the 74th parallel. And the best time to do this is in July.
The outlines of the Shield resemble, indeed, a shield. You can navigate by the Tail of the Serpent and the constellation Eagle. In general, the Shield is completely projected onto the Milky Way, so it is rather problematic to see this scattering of several dim stars.
Alpha Shield has its own name - Ioannina. It is an orange giant of magnitude 4.
Beta Scuti is a binary star consisting of a bright yellow giant and a blue-white companion. The star is 690 light years away from Earth.
Of the objects of deep space in the composition of the Shield, two star clusters can be noted. One of them is called Wild Duck. This is one of the most star-rich clusters in the sky.
Telescope

The Telescope completes the five of the August constellations. It is located in the southern hemisphere, covers an area of 252 square degrees and contains about 50 stars that can be distinguished without the help of optical instruments.
The outline of the Telescope resembles an elongated line, which is located north of the Altar and south of the South Crown. You can see it only in the southern hemisphere, and on the territory of Russia it is not observed.
The brightest stars in the Telescope are only 4 and 5 magnitudes. Alpha Telescope is a blue-white subgiant, 249 light-years from Earth.
The constellation contains several double stars, and Xi Telescope is an irregular variable star unique in its kind.
Of the distant space objects, the Telescope includes a globular cluster, which can be observed in the western part of the constellation.
Page 2 of 4
This article discusses what types and forms of clouds are.
The first criterion by which clouds are divided when answering the question: What are clouds? is the location height.
Height dependent locations are as follows types of clouds:
- Upper clouds (Ci, Cs, Cc)- types of clouds located at an altitude of more than 6000 meters from the surface of the earth. You can already observe them from a distance of 100-200 km, they usually appear from the side where the cyclone comes from;
- Middle tier clouds (As, Ac)- types of clouds that occur at an altitude of 2000 to 6000 meters. They differ from the clouds of the previous type by the larger size of cloud elements, the color gray color and casting a shadow on the surface of the earth - due to their greater density, they weakly transmit sunlight or moonlight;
- Clouds lower tier(Cu, Sc, St)– types of clouds located at an altitude of less than 2000 meters. They sometimes lag behind the clouds of the upper tier by 400-500 km, from the middle tier - by 200-300 km. They are distinguished by a dark saturated color, cast a thick shadow due to complete opacity. They swim low in the form of huge ridges or a continuous veil. Precipitation falls from lower clouds.
- Clouds of vertical development (Ns, Cb). The lower part of this type of cloud (white, gray or dark gray) can be below 2000 meters, and the top (always white) reaches a level of 6-8 thousand meters. By appearance they are dense cloud masses with flat bases.
The answer to the question: What are clouds? is not limited to listing types of clouds by altitude. In turn, the listed types of clouds are different in shape.
So, the shape of the clouds are ...
Cloud shapes. What are clouds?
What are the clouds of the upper tier in shape:
Spindrift clouds,
cirrocumulus clouds,
Cirrostratus clouds.
 Cirrus clouds (Cirrus, Ci
Cirrus clouds (Cirrus, Ci
Color:
white.
Description and shape of the cloud.
These clouds are of a delicate white color in the form of threads, feathers, wavy ribbons. Slightly silver tint. They have a fairly large vertical length - up to several kilometers. However, due to the action of the wind, they are strongly curved. Cirrus clouds are characterized by a rare but very beautiful phenomenon called "fiery rainbow".
Visibility inside the cloud
: 150-500 meters.
Composition and education
. Made up of ice crystals. They form in front of a cloud mass of a warm front or an occlusion front. They are also characteristic of anticyclonic conditions, and sometimes remain from ice peaks (anvils) of cumulonimbus clouds.
Precipitation never falls from cirrus clouds.
Cirrocumulus (Cirrocumulus, Cc) is a type of upper layer clouds.

Color:
white.
Description and shape of the cloud
.
There are lambs, lambs, lambs in the sky ... This is exactly them. These clouds are small in size, oval, lined up, they float high, high above the ground. Reminds me of ripples in the sand. Do not cast shadows, harbingers of rising temperatures. In cirrocumulus clouds, the effect of halo and crowns around the sun and moon can occur.
Visibility inside the cloud
: 200-500 meters.
Composition and education
. Source of material for education pinnate cumulus clouds- wave and ascending air currents. The cloud element is ice crystals.
Cloud weather prediction.
For good weather. Most often, they disperse and expose the blue sky.
 Deformed cirrocumulus clouds.
Deformed cirrocumulus clouds.
Sometimes rounded breaks can be observed in cirrocumulus clouds. Such a gap is formed when the temperature in the cloud is below zero, but the water has not yet had time to freeze. When water begins to freeze in one place, the nearby water vapor quickly evaporates and condenses on ice crystals. Ice crystals become heavy and under their own weight can settle to the ground. Thus, deformed cirrocumulus clouds are obtained.
Cirrostratus clouds (Cirrostratus, Cs) - a type of clouds of the upper tier.
Color:
whitish, translucent.
Description and shape of the cloud
.
Cirrostratus clouds are in the form of a continuous veil high in the sky. In the presence of these clouds, the sun and moon float as if in a haze. The transparency of clouds can vary depending on the density of the cloud. At low density, the halo effect is also observed. The thickness of cirrostratus clouds can reach 2-6 kilometers.
Visibility inside the cloud
: 50-200 meters.
Composition and education.
The source of material for the formation of cirrostratus clouds is whole layers of air rising upward as a result of multilevel convergence. The cloud element is ice crystals.
Cloud weather prediction.
Precipitation does not fall out of them, but thickening of cirrostratus clouds can serve as a harbinger of bad weather.
What are the middle tier clouds in shape:
altocumulus clouds,
altostratus clouds,
Altostratus translucent clouds.
Altocumulus clouds(Altocumulus, Ac
Color
: white, gray or bluish white.
Description and shape of the cloud
. Altocumulus clouds are usually summer time. They are arranged in waves or in ridges in the form of flakes or plates. There are gaps between individual elements. Sometimes around these clouds there is a beautiful phenomenon called "iridization"
. This is the iridescent coloration of the edge of the cloud.
Visibility inside the cloud
: 50-80 meters.
Composition and education.
Formed when warm air rises. The rise can be provoked by the onset of a cold front, which displaces air heated near the surface of the earth upward.
Cloud weather prediction.
Appear after a thunderstorm or storm. They predict clear weather.
Altostratus clouds (Altostratus, As) - a type of clouds of the middle tier.
Color
: gray or bluish.
Description and shape of the cloud
. Altostratus clouds are in the form of a uniform or slightly wavy veil through which the sun and moon faintly shine through. Cloud height varies from one to four kilometers.
Visibility inside the cloud
: 25-40 meters.
Composition and education.
The main cloud elements are ice crystals, snowflakes, supercooled water.
Cloud weather prediction.
Precipitation falls from altostratus clouds. This is heavy rain or snow.
Altostratus translucent clouds (Altostratus translucidus, As trans) - a type of middle tier clouds
.
Color
: white-bluish.
Description and shape of the cloud
. Clearly visible translucent wavy stripes. The solar and lunar disks are quite distinct. Despite this, they cast a faint shadow on the ground. The lower boundary of these clouds is at an altitude of 3-5 km. The height of the cloud array is 1-2 km. Gradually cover the entire sky with a continuous veil.
Cloud weather prediction.
Precipitation also falls from altostratus translucent clouds, but in summer it rarely reaches the earth's surface.
What are the clouds of the lower tier in shape:
layered clouds,
stratocumulus clouds,
Cumulus clouds.
Stratus clouds (Stratus, St) - a type of clouds of the lower tier.
Color
: dark gray or light gray.
Description and shape of the cloud
. Layered clouds are in the form of a homogeneous whitish veil that covers the entire sky and looks like fog. The height of the cloud is small - from several tens to hundreds of meters. The lower part can drop very low, and then the cloud merges with the fog. Formed in the lower troposphere.
: 100-400 meters, sometimes drops to 30-90.
Cloud weather prediction.
Stratus clouds occasionally produce precipitation. It's drizzle or snow grains, depending on the season.
Stratocumulus clouds (Stratocumulus, Sc) - a type of clouds of the lower tier.
Color
: grey.
Description and shape of the cloud
. Stratocumulus clouds are in the form of massive ridges, waves, plates. They can be both with gaps, and tighten the sky with a continuous wavy veil. The height of the cloud layer is from 200 to 800 meters. Quite dense, the sun shines through only at the edges of the clouds.
Height above ground
: 500 to 1800 meters.
Compound
. The main cloud element is water drops.
Cloud weather prediction.
Precipitation is possible only occasionally, and even then short.
Striped stratocumulus clouds.
Color
: grey.
Description and shape of the cloud
. A variety of stratocumulus clouds. They are notable for the fact that they are located in the sky in the form of regular rows or waves separated by gaps.
Height above ground
: 500 to 1800 meters.
Compound
. The cloud element is water drops.
Cloud weather prediction.
Most often they portend good weather.
Cumulus clouds (Cumulus, Cu) - a type of clouds of the lower tier.
Color
: bright white.
Description and shape of the cloud
. Dense, elongated clouds. The upper part of cumulus clouds is rounded or in the form of round turrets.
Height above ground
: from 800 to 1500 meters, occasionally more than two kilometers.
Cloud weather prediction.
If they are located separately, far from each other, then to good weather. But if the cumulus clouds are large and multi-storey, then there may be a heavy downpour.
What are the clouds of vertical development in shape:
nimbostratus clouds,
Cumulonimbus clouds.
Nimbostratus clouds (Nimbostratus, Ns) - a type of clouds of vertical development.

Color
: dark gray, with a bluish tint.
Description and shape of the cloud
. Clouds cover the earth in a continuous veil. Nimbostratus clouds are heterogeneous structure, sometimes wavy. The thickness of the layer is up to several kilometers. They differ from stratus clouds in their heterogeneous structure, which becomes blurred during rain or snow. But in the intervals between precipitation, the heterogeneity again becomes discernible.
Height above ground
: 100 to 1900 meters.
Cloud weather prediction.
They produce heavy rainfall.
Cumulonimbus (Cumulonimbus, Cb) — type of clouds of vertical development
.
Color
: thick dark grey.
Description and shape of the cloud
. Powerful dense clouds reaching a height of more than 10 km. Clouds are preceded by a squally wind, a hurricane. They are distinguished by a flat top - an "anvil", consisting of ice crystals.
Height above ground
: up to 2000 meters.
Compound
. At the base - water drops, and at the top, where the temperature is much lower - ice crystals.
Cloud weather prediction.
Cumulonimbus clouds are the harbinger of bad weather. They bring heavy rain, thunderstorms, hail is possible.
This completes the enumeration of the main types and the shape of the clouds, but there are other, rarer types. They cannot be assigned to any of the above categories, therefore they are considered separately. In the next article, we will answer the question: What other clouds are there?
It was the article “Types and forms of clouds. What are clouds? Read further: Rare types of clouds. What else are clouds?
Cirrus clouds (Cirrus, Ci) have a thickness from hundreds of meters to several kilometers. They consist of ice crystals in the form of needles, columns, plates. The luminaries shine through them. There are such types of cirrus clouds: filiform, claw-shaped, tower-shaped, dense, flaky, entangled, radial, ridge-like, double .
cirrocumulus clouds (Cirrocumulus, Cc) are characterized by a small width - 200–400 m. The structure of the clouds is lumpy. They are transparent. There are wavy, cumulus with turrets, flaky varieties of cirrocumulus clouds.
Cirrostratus clouds (Cirrostratus, Cs) they look like a white or bluish translucent shroud. Their thickness ranges from 100 m to several kilometers.
Altocumulus (Altocumulus, Ac) they look like white, sometimes grayish waves, consisting of plates or flakes separated by gaps in the blue sky, but they can also merge into a continuous cover. The thickness of the layer of altocumulus clouds is about 200–700 m. Rain and snow fall out of them.
Altostratus clouds (Altostratus, As) form a solid gray or bluish "carpet" in the sky with a lower boundary, usually at an altitude of 3–5 km. The thickness of the cloud layers is 1–2 km.
High-layered translucent (Altostratus translucidus, As trans)
Stratocumulus clouds (Nimbostratus, Ns) - this is gray clouds, consisting of large ridges, waves, plates, separated by gaps or merging into a continuous gray wavy cover. They consist mainly of drops. The layer thickness is from 200 to 800 m. Precipitation, as a rule, does not fall. Stratocumulus clouds are wavy, cumulus, dissecting, vymeobrazny.
Stratus clouds (Stratus, St) they are a uniform gray or gray-yellow cover. There are different types: foggy, wavy and broken. Broken rain clouds are often observed under a veil of stratus clouds.
Nimbostratus the clouds look like a solid gray veil that covers the entire sky in the form of ridges and shafts. They consist of water droplets, rarely mixed with snowflakes. Heavy precipitation falls from this type of cloud.
Cumulus clouds (Cumulus, Cu) divided into cumulus, cumulus medium and cumulus powerful. Thickness 1-2 km, sometimes 3-5 km. The upper parts of cumulus clouds look like domes or towers with rounded outlines.
Cumulonimbus (Cumulonimbus, Cb)- very powerful cloud clusters; they are "bald" and "hairy", with a thunderous arcuate shaft in front.
Clouds of an unusual shape
are rare, most often in the tropics. Their appearance is associated with the formation of tropical cyclones.
also a very rare occurrence.

This article lists and describes all types of clouds.
Cloud types
Upper clouds formed in temperate latitudes above 5 km, in polar regions - above 3 km, in tropical regions - above 6 km. The temperature at this altitude is quite low, so they consist mainly of ice crystals. Upper clouds are usually thin and white. The most common form of upper clouds are cirrus (cirrus) and cirrostratus (cirrostratus), which can usually be observed in good weather.
Middle clouds usually located at an altitude of 2-7 km in temperate latitudes, 2-4 km in polar and 2-8 km in tropical latitudes. They consist mainly of small particles of water, but at low temperatures they can also contain ice crystals. The most common types of mid-tier clouds are altocumulus (altocumulus), altostratus (altostratus). They may have shaded portions, which distinguishes them from cirrocumulus clouds. This type of cloud usually results from air convection and also from the gradual rise of air ahead of a cold front.
Lower clouds located at altitudes below 2 km, where the temperature is quite high, so they consist mainly of water droplets. Only in the cold season. When the surface temperature is low, they contain particles of ice (hail) or snow. The most common types of low clouds are nimbostratus (Nimbostratus) and Stratocumulus (stratocumulus) - dark clouds lower tier, accompanied by moderate precipitation.
Fig1. The main types of clouds: Cirrus, Ci), Cirrocumulus (Cirrocumulus, Cc), Cirrostratus, Cs, Altocumulus (Altocumulus, Ac), Altostratus, As, Altostratus translucidus , As trans) , Strato-nimbus (Nimbostratus, Ns), Stratus (Stratus, St) , Stratocumulus (Stratocumulus, Sc), Cumulus (Cumulus, Cu), Cumulonimbus (Cumulonimbus, Cb)
Pinnate (Cirrus, Ci)
They consist of separate pinnate elements in the form of thin white threads or white (or mostly white) tufts and elongated ridges. They have a fibrous structure and / or a silky sheen. They are observed in the upper troposphere, in the middle latitudes their bases most often lie at altitudes of 6-8 km, in the tropical from 6 to 18 km, in the polar from 3 to 8 km). Visibility within the cloud is 150-500 m. They are built from ice crystals large enough to have an appreciable falling speed; therefore, they have a significant vertical extent (from hundreds of meters to several kilometers). However, wind shear and differences in crystal size cause the filaments of cirrus clouds to be slanted and warped. These clouds are typical for leading edge a cloudy system of a warm front or an occlusion front associated with an upward slip. They often also develop in anticyclonic conditions, sometimes they are parts or remnants of ice tops (anvils) of cumulonimbus clouds.
There are different types: filiform(Cirrus fibratus, Ci fibr.), claw-like(Cirrus uncinus, Ci unc.), turret-shaped(Cirrus castellanus, Ci cast.), dense(Cirrus spissatus, Ci spiss.), flaky(Cirrus floccus, Ci fl.) and varieties: mixed up(Cirrus intortus, Ci int.), radial(Cirrus radiatus, Cirad.), spinal(Cirrus vertebratus, Ci vert.), double(Cirrus duplicatus, Ci dupl.).
Sometimes this genus of clouds, along with the described clouds, also includes cirrostratus and cirrocumulus clouds.
Cirrocumulus (Cirrocumulus, Cc)
They are often referred to as "lambs". Very high small globular clouds, elongated in a line. Look like the backs of mackerels or ripples on the coastal sand. The height of the lower border is 6-8 km, the vertical length is up to 1 km, the visibility inside is 5509-10000 m. They are a sign of an increase in temperature. Often observed together with cirrus or cirrostratus clouds. They are often the forerunners of storms. With these clouds, the so-called. "iridization" - iridescent coloring of the edge of the clouds.
Cirrostratus, Cs
Halo formed on cirrus clouds
Sail-like clouds of the upper tier, consisting of ice crystals. They have the appearance of a homogeneous, whitish veil. The height of the lower edge is 6-8 km, the vertical extent varies from several hundred meters to several kilometers (2-6 or more), visibility inside the cloud is 50-200 m. Cirrostratus clouds are relatively transparent, so the sun or moon can be clearly visible through them. These upper tier clouds usually form when large layers of air rise up through multilevel convergence.
Cirrostratus clouds are characterized by the fact that they often give the phenomena of a halo around the sun or moon. Halos are the result of the refraction of light by the ice crystals that make up the cloud. Cirrostratus clouds, however, tend to thicken as a warm front approaches, which means more ice crystal formation. As a result, the halo gradually disappears, and the sun (or moon) becomes less visible.
Altocumulus (Altocumulus, Ac)
Formation of altocumulus clouds.
Altocumulus (Altocumulus, Ac) - typical warm season cloud cover. Gray, white, or bluish clouds in the form of waves and ridges, consisting of flakes and plates separated by gaps. The height of the lower boundary is 2-6 km, the vertical length is up to several hundred meters, the visibility inside the cloud is 50-80 m. They are usually located above the places facing the sun. Sometimes they reach the stage of powerful cumulus clouds. Altocumulus clouds usually form as a result of the rise of warm air masses, as well as the onset of a cold front, which displaces warm air up. Therefore, the presence of altocumulus clouds on a warm and humid summer morning portends the imminent appearance of storm clouds or a change in the weather.
High-stratified (Altostratus, As)
Altostratus clouds
They look like a uniform or weakly expressed wavy veil of gray or bluish color, the sun and moon usually shine through, but weakly. The height of the lower boundary is 3-5 km, the vertical extent is 1-4 km, the visibility in the clouds is 25-40 m. These clouds consist of ice crystals, supercooled water drops and snowflakes. Altostratus clouds can bring heavy rain or snow.
High-layered translucent (Altostratus translucidus, As trans)
Altostratus clouds at sunset
Altostratus translucent clouds. The wavy structure of the cloud is noticeable, the solar circle of the sun is quite distinguishable. Quite distinguishable shadows can sometimes appear on the ground. Stripes are clearly visible. A veil of clouds, as a rule, gradually covers the entire sky. The height of the base is within 3-5 km, the thickness of the As trans cloud layer is on average about 1 km, occasionally up to 2 km. Precipitation falls, but in low and middle latitudes it rarely reaches the ground in summer.
Nimbostratus (Nimbostratus, Ns)
Nimbostratus clouds and strong air currents.
Nimbostratus clouds are dark gray, in the form of a continuous layer. During precipitation, it seems to be homogeneous; in the intervals between precipitation, some heterogeneity and even some undulation of the layer are noticeable. They differ from stratus clouds in their darker and bluish color, inhomogeneity of the structure and the presence of extensive precipitation. The height of the lower boundary is 0.1-1 km, the thickness is up to several kilometers.
Layered (Stratus, St)
Layered clouds.
Layered clouds form a homogeneous layer, similar to fog, but located at a height of hundreds or even tens of meters. Usually they cover the entire sky, but sometimes they can be observed in the form of broken cloud masses. The lower edge of these clouds can drop very low; sometimes they merge with ground fog. Their thickness is small - tens and hundreds of meters.
Stratocumulus (Stratocumulus, Sc)
Gray clouds, consisting of large ridges, waves, plates, separated by gaps or merging into a continuous gray wavy cover. Composed primarily of water droplets. The thickness of the layer is from 200 to 800 m. The sun and moon can only shine through the thin edges of the clouds. Precipitation usually does not fall. From stratocumulus clouds that are not translucent, weak, short-term precipitation may fall.
Cumulus clouds (Cumulus, Cu)
Cumulus clouds. View from above.
Cumulus clouds are dense, bright white clouds during the day with a significant vertical development(up to 5; km and more). The upper parts of cumulus clouds look like domes or towers with rounded outlines. Cumulus clouds usually form as convection clouds in cold air masses.
Cumulonimbus (Cumulonimbus, Cb)
Cumulonimbus (Cumulonimbus capillatus incus)
Cumulonimbus - powerful and dense clouds with a strong vertical development (up to a height of 14 km), giving heavy rainfall with powerful hail and thunderstorms. Cumulonimbus clouds/clouds develop from powerful cumulus clouds. They can form a line called a squall line. The lower levels of cumulonimbus clouds are mostly water droplets, while the higher levels, where temperatures are well below 0°C, are dominated by ice crystals.




