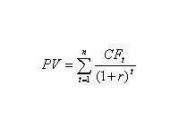An increase in the present value of technological equipment leads to. Present value. About the accuracy of calculating the discount rate
They play a vital role in the development of the economy and increasing its competitiveness. The problem of giving them a dynamic and non-alternative character is very relevant for modern Russia. With their help, a qualitatively new level of means of production is achieved, its volumes are increased, and innovative technologies are developed.
Is the topic of investment relevant for Russia? Perhaps the answer to this question will be the information from Rosstat for 2013, indicating that the annual flow of foreign investment into the country’s economy increased by 40% compared to last year. In general, accumulated foreign capital in the Russian economy at the end of last year amounted to 384.1 billion US dollars. The majority of investments (38%) are in the manufacturing industry. 18% of their volume is invested in trade and repairs, almost the same amount (17%) in the mining industry.
According to statistics, since 2012, economic observers have determined that Russia ranks sixth in the world in terms of its investment attractiveness and at the same time is the leader among the CIS countries in this indicator. In the same 2012, foreign direct investment in the Russian market covered 128 large objects. The dynamics of the process are obvious. Already in 2013, according to Rosstat, the volume of foreign direct investment in the Russian economy alone increased by 10.1% and reached $170.18 billion.
There is no doubt that all these investments are being made in a meaningful way. The investor preliminary, before investing his funds, of course, evaluates the attractiveness of the project commercially, financially, technically, socially.
Investment attractiveness
The above statistics also have a “technical” side. This process is deeply understood according to the well-known principle, according to which you must first measure seven times. The essence of investment attractiveness as an economic category lies in the benefit predetermined by the investor immediately before investing his capital in a specific company or project. When investing, attention is paid to the solvency and financial stability of the startuper at all stages of the development of the funds invested in it. Therefore, the structure of the investment itself, as well as its flows, must, in turn, be optimized.
This is achievable if the company making such an investment systematically carries out strategic management of investments in the startup. The latter is:
- a sober analysis of the long-term goals of its development;
- formation of an investment policy adequate to them;
- its implementation in compliance with the necessary control with constant cost adjustment in relation to market conditions.
The previous volume of the startup is studied, the possibility of reducing current costs and increasing the technological level of production is considered as a priority.
When forming a strategy, the legal conditions for its implementation are necessarily taken into account, the level of corruption in the economic segment is assessed, and a forecast of the market situation is carried out.
Methods for assessing investment attractiveness
They are divided into static and dynamic. When using static methods, a significant simplification is allowed - the cost of capital is constant over time. The effectiveness of static capital investments is determined by their payback period and efficiency ratio. However, such academic indicators are of little use in practice.
In the real economy, dynamic indicators are more often used to evaluate investments. The topic of this article will be one of them - net present value (NPV, also known as NPV). It should be noted that, in addition to it, they use such dynamic parameters as:
But still, among the above indicators, in practice, the central place remains with net present value. Perhaps the reason is that this parameter allows you to correlate cause and effect - capital investments with the amount of cash flows they generate. The feedback contained in its content has led to the fact that NPV is perceived as a standard investment criterion. What does this indicator still underestimate? We will also consider these questions in the article.
Fundamental formula for determining NPV
Referred to as discounted cash flow methods or DCF methods. Its economic meaning is based on a comparison of IC investment costs and adjusted future cash flows. Fundamentally, the NPV is calculated as follows (see formula 1): NPV = PV - Io, where:
- PV - current value of cash flow;
- Io is the initial investment.
The above NPV formula shows cash income in a simplified way.
Formula taking into account discount and one-time investment
Of course, the above formula (1) should be complicated, if only to show the discounting mechanism in it. Since the influx of financial resources is distributed over time, it is discounted using a special coefficient r, which depends on the cost of investment. By discounting the parameter, a comparison of cash flows that differ in time of occurrence is achieved (see formula 2), where:

The NPV formula should take into account the adjusted discount (coefficient r), determined by the investor’s analysts in such a way that both the inflow and outflow of funds are taken into account for the investment project in real time.
According to the methodology described above, the relationship between investment efficiency parameters can be represented mathematically. What pattern does the formula that defines the essence of NPV express? That this indicator reflects the cash flow received by the investor after the implementation of the investment project and the recoupment of the costs provided for in it (see formula 3), where:
- CF t - investment payments for t years;
- Io - initial investment;
- r - discount .

Given above) is calculated as the difference between the total cash receipts updated at a certain point in time for risks and the initial investment. Therefore, its economic content (meaning the current version of the formula) is the profit received by the investor with a powerful one-time initial investment, i.e. the added value of the project.
In this case, we are talking about the NPV criterion. Formula (3) is a more realistic tool for a capital investor, considering the possibility of making an investment from the point of view of subsequent benefits. Operating with cash flows updated at the current time, it is an indicator of benefit for the investor. Analysis of its results really influences his decision: to invest or abandon them.
What do negative NPV values tell an investor? That this project is unprofitable and investments in it are unprofitable. It has the opposite situation with a positive NPV. In this case, the investment attractiveness of the project is high, and accordingly, such an investment business is profitable. However, it is possible that the net present value is zero. It is curious that investments are made under such circumstances. What does this NPV indicate to the investor? That his investment will expand the company's market share. It will not bring profit, but it will strengthen the state of the business.
Net present value for a multi-step investment strategy
Investment strategies change the world around us. The famous American writer and businessman Robert Kiyosaki said well on this topic that it is not the investment itself that is risky, but the lack of management of it. At the same time, the constantly progressing material and technical base forces investors not to make one-time, but to periodic investments. The NPV of the investment project in this case will be determined by the following formula (3), where m is the number of years during which the investment activity will be carried out, I is the inflation rate.

Practical use of the formula
Obviously, making calculations using formula (4) without using auxiliary tools is a rather labor-intensive task. Therefore, it is quite common practice to calculate return on investment indicators using spreadsheet processors created by specialists (for example, implemented in Excel). It is typical that to assess the NPV of an investment project, several investment flows should be taken into account. At the same time, the investor analyzes several strategies at once in order to finally understand three questions:
- -what volume of investment is needed and in how many stages;
- -where to find additional sources of financing and lending if necessary;
- -whether the volume of projected revenues exceeds the costs associated with investments.
The most common way to practically calculate the real viability of an investment project is to determine the NPV 0 parameters for it at (NPV = 0). The tabular form allows investors, without wasting extra time, without seeking the help of specialists, to visually present various strategies in a minimum amount of time and, as a result, choose the most efficient option for the investment process.
Using Excel to Determine NPV
How in practice do investors make forecast NPV calculations in Excel? We will present an example of such a calculation below. Methodological support for the very possibility of determining the effectiveness of the investment process is based on a specialized built-in NPV() function. This is a complex function that works with several arguments typical of the net present value formula. Let's demonstrate the syntax of this function:
NPV(r; Io;C4:C11), where (5) r is the discount rate; Io - initial investment
CF1: CF9 - project cash flow for 8 periods.
CF investment project stage | Cash flow (thousand rubles) | Discount | Net Present Value NPV |
186.39 thousand rubles. |
|||
In general, based on an initial investment of RUB 2.0 million. and subsequent cash flows at nine stages of the investment project and a discount rate of 10%, net present value NPV will be 186.39 thousand rubles. The dynamics of cash flows can be presented in the form of the following diagram (see diagram 1).
Diagram 1. Cash flows of an investment project

Thus, we can draw a conclusion about the profitability and prospects of the investment shown in this example.
Net present value chart
A modern investment project (IP) is now considered by economic theory in the form of a long-term calendar plan for capital investments. At each time stage it is characterized by certain income and costs. The main item of income is the proceeds from the sale of goods and services, which are the main purpose of such an investment.
To construct an NPV chart, you should consider how this function behaves (the importance of cash flows) depending on the argument - the duration of investments of different NPV values. If for the above example, then at its ninth stage we obtain the total value of private discounted income of 185.39 thousand rubles, then, limiting it to eight stages (say, by selling the business), we will achieve a NPV of 440.85 thousand rubles. Seven - we will enter a loss (-72.31 thousand rubles), six - the loss will become more significant (-503.36 thousand rubles), five - (-796.89 thousand rubles), four - ( -345.60 thousand rubles), three - (-405.71 thousand rubles), limited to two stages - (-1157.02 thousand rubles). These dynamics show that the NPV of the project tends to increase in the long term. On the one hand, this investment is profitable, on the other hand, the investor’s sustainable profit is expected from approximately the seventh stage (see diagram 2).
Diagram 2. NPV chart

Selecting an investment project option
When analyzing Diagram 2, two alternative options for a possible investor strategy are revealed. Their essence can be interpreted extremely simply: “What to choose - a smaller profit, but immediately, or a larger one, but later?” Judging by the graph, NPV (net present value) temporarily reaches a positive value at the fourth stage of the investment project, however, subject to a longer investment strategy, we enter the phase of sustainable profitability.
In addition, we note that the NPV value depends on the discount rate.
What does the discount rate take into account?
One of the components of formulas (3) and (4), by which the NPV of a project is calculated, is a certain discount percentage, the so-called rate. What does it show? Mainly the expected inflation index. In a sustainable society it is 6-12%. Let's say more: the discount rate directly depends on the inflation index. Let us recall a well-known fact: in a country where it exceeds 15%, investments become unprofitable.
We have the opportunity to check this in practice (we do have an example of calculating NPV using Excel). Let us remember that the NPV indicator we calculated at a discount rate of 10% at the ninth stage of the investment project is 186.39 thousand rubles, which demonstrates profit and interests the investor. Let's replace the discount rate in the Excel table with 15%. What will the NPV() function show us? The loss (and this at the end of the nine-stage process is 32.4 thousand rubles. Will the investor agree to a project with a similar discount rate? Not at all.
If we conditionally reduce the discount to 8% before calculating NPV, then the picture will change to the opposite: net present value will increase to 296.08 thousand rubles.
Thus, there is a demonstration of the advantages of a stable economy with low inflation for successful investment activity.
Largest Russian investors and NPV
What are the consequences of investors successfully accounting for winning strategies? The answer is simple - to success! Let's present the rating of the largest Russian private investors based on last year's results. The first position is occupied by Yuri Milner, co-owner of Mail.ru Group, who founded the DTS fund. He successfully invests in Facebook, Groupon Zygna. The scale of its capital investments is adequate to modern world ones. Perhaps that is why he occupies 35th position in the world ranking, the so-called Midas List.

The second position goes to Viktor Remsha, who made a brilliant deal in 2012 to sell 49.9% of the Begun service.
The third position is occupied by the co-owner of about 29 Internet companies, including the Ozon.ru megamarket. As we can see, the three largest domestic private investors are investing in Internet technologies, i.e., the sphere of intangible production.
Is this specialization accidental? Using the tools for determining NPV, let's try to find the answer. The above investors, due to the specifics of the Internet technology market, automatically enter the market with a smaller discount, maximizing their benefits.
Conclusion
Modern business planning, in terms of calculations of return on investment and sensitivity to changes in expenses, currently widely uses preliminary efficiency analysis, including the determination of net present value. For investors, it is of great importance to determine the sustainability of the indicators of the basic version of the investment project.

The universality of NPV makes it possible to do this by analyzing the change in the parameters of an investment project at its zero value. In addition, this is a fairly technologically advanced tool, implemented for a wide range of users in standard spreadsheet processors using the functions built into them.
It is so popular that there are even online calculators for determining it on the Russian-language Internet. However, Excel tools allow you to analyze more investment strategy options.
Net present value (NPV) is one of the main indicators on the basis of which financial decisions are made. Typically NPV is used to evaluate the performance of an investment over the long term. This indicator is most often used in the field of corporate finance, but it is also useful for daily monitoring of the financial situation. Net present value is calculated using the formula (P / (1 + i) t) – C, where t is the number of time periods, P is the flow of payments, C is the amount of initial investment, i is the discount rate.
Steps
Part 1
NPV calculation- For example, let's say you own an orange juice stand. Are you thinking about purchasing an electric juicer that will help you increase your juice production. If a juicer costs $100, then $100 is an initial investment. Over time, this initial investment will allow you to earn more money. By calculating the NPV, you will determine whether the juicer is worth purchasing.
-
Decide what time period you will analyze. For example, if a shoe factory buys additional equipment, then the purpose of this purchase is to increase production and make more money over a certain period of time (until the equipment fails). Therefore, to calculate NPV, you need to know the period of time during which the investment must pay off. A period of time can be measured in any time unit, but in most cases one time period is considered to be one year.
- In our example, the warranty on the juicer is given for 3 years. In this case, the number of time periods is 3, since after 3 years the juicer will most likely break down and will not be able to generate additional profit.
-
Determine the flow of payments during one time period, that is, the cash receipts that are generated due to the investments made. The payment stream can be a known value or an estimate. If this is an estimate, then companies and financial firms spend a lot of time and hire relevant specialists and analysts to obtain it.
- For our example, let's say you think that purchasing a $100 juicer will generate an additional $50 in the first year, $40 in the second year, and $30 in the third year (by reducing the time your employees spend juicing and the corresponding wage costs). . In this case, the payment flow is: $50 for year 1, $40 for year 2, $30 for year 3.
-
Determine the discount rate. In general, any amount has more value now than in the future. You can put this amount in the bank today and receive it in the future with interest (that is, $10 today is worth more than $10 in the future, since you can invest $10 today and get more than $11 in the future). To calculate NPV, you must know the interest rate on an investment account or investment opportunity with a similar level of risk. This interest rate is called the discount rate; To calculate NPV it must be converted to a decimal fraction.
- Companies often use the weighted average cost of capital to determine the discount rate. In simple situations, you can use the rate of return on a savings account, investment account, etc. (that is, an account in which you can deposit money at interest).
- In our example, let's say that if you don't buy a juicer, you invest your money in the stock market, where you will earn 4% per annum on the amount invested. In this case, 0.04 (4% as a decimal) is the discount rate.
-
Discount cash flow. This can be done using the formula P / (1 + i)t, where P is cash flow, i is interest rate and t is time. Now you don’t have to think about the initial investments - they will be useful in further calculations.
- In our example, the number of time periods is 3, so use the formula three times. Calculate the annual discounted cash flows as follows:
- Year 1: 50 / (1 + 0.04) 1 = 50 / (1.04) = $48,08
- Year 2: 40 / (1 +0.04) 2 = 40 / 1.082 = $36,98
- Year 3: 30 / (1 +0.04) 3 = 30 / 1.125 = $26,67
- In our example, the number of time periods is 3, so use the formula three times. Calculate the annual discounted cash flows as follows:
-
Add up the resulting discounted cash flows and subtract the initial investment from the total. What you'll end up with is the NPV, which is the amount of money the investment will make compared to the amount that alternative investments would make you at the discount rate. In other words, if it is a positive number, then you will make more money from the investment than from the alternative investment (and vice versa if the number is negative). But remember that the accuracy of the calculation depends on how accurately you estimate future cash flows and the discount rate.
- In our example, NPV is calculated as follows:
- 48,08 + 36,98 + 26,67 - 100 = $11,73
- In our example, NPV is calculated as follows:
-
If NPV is a positive number, then the project will be profitable. If the NPV is negative, then you should invest the money somewhere else or reconsider the project. In the real world, NPV allows you to decide whether it is worth investing in a particular project at all.
- In our example, NPV = $11.73. Since this is a positive number, you will most likely decide to buy a juicer.
- Note that this figure does not mean that the electric juicer will only net you $11.73. What this actually means is that the juicer will earn you $11.73 more than what you would get by investing in the stock market at 4% per annum.
Part 2
Using the formula to calculate NPV-
By calculating the NPV of several investment projects, you can compare their effectiveness. Investments with high NPV are more effective, so invest in projects with the highest NPV (unless you have sufficient funds to invest in each project).
- For example, you are considering three investment projects. One has an NPV of $150, the second has an NPV of $45, and the third has an NPV of -$10. In this situation, invest in a project with an NPV of $150, and only then invest in a project with an NPV of $45. Do not invest in a project with NPV = -$10, since a negative value indicates that it is better to invest in an alternative project with a similar level of risk.
-
Use the formula PV = FV / (1+i)t to calculate the "present" and "future" value of an investment. In this formula, i is the discount rate, t is time, FV is future value, PV is present value.
- For example, let's calculate the value of a $1,000 investment after five years. Let's assume that these funds can be invested (as an alternative) at 2% per annum. In this case i = 0.02; t = 5, PV = 1000.
- 1000 = FV / (1+0.02) 5
- 1000 = FV / (1.02) 5
- 1000 = FV / 1.104
- 1000 x 1.104 = FV = $1104 .
- For example, let's calculate the value of a $1,000 investment after five years. Let's assume that these funds can be invested (as an alternative) at 2% per annum. In this case i = 0.02; t = 5, PV = 1000.
-
Find out what valuation methods exist to obtain a more accurate NPV value. As noted above, the accuracy of the NPV calculation depends on the accuracy of the quantities you use to estimate the discount rate and future payment streams. If the discount rate is close to the interest rate of an alternative investment (with a similar level of risk), and the future cash flows are close to the amounts you will actually receive (as a result of the investment), then the calculated NPV value will be quite accurate. To estimate the required values as accurately as possible, learn about the corporate valuation methods that are used by large corporations when analyzing huge multi-million dollar investment projects.
- Always remember that there are other, non-financial factors (such as environmental or social) that need to be taken into account when making any investment decision.
- NPV can also be calculated using a financial calculator or NPV tables, which are useful if you don't have a financial calculator.
Determine the amount of initial investment. Investments are often made to generate profits over the long term. For example, a construction company might buy a bulldozer to take on larger projects and make more money from them. Such investments always have an initial size.
Galtsev Dmitry Alexandrovich
The term “net present value” usually denotes the value of the total discounted values of payment flows, the value of which is given in real time (as of today).
Short abbreviation, NPP. In the specialized literature, other names for this quantity are often used.
For example:
- NPV (net present value). This name is explained by the fact that the flows in question are first discounted and only then added up;
- NPV (net present value). Discounting brings all financial flows to the real (today's) value of money.
International designation – NPV.
Economic meaning of NPV indicator
If we consider the indicator more deeply, we can state that this is the resulting value obtained by taking into account all outgoing and incoming cash receipts of the analyzed investment project, reduced to the time of such analysis.
The resulting value gives the investor an idea of what he can expect when investing (taking into account the repayment of initial costs incurred at the initial stage of project development and periodic outflows during its implementation).
Due to the fact that all cash flows are calculated taking into account risks and time value, the NPV value of an investment project can be characterized as the value added by the project, or as the total profit of the investor.
The main goal of any business is to make a profit.
In order not to invest in risky projects, the investor conducts a preliminary assessment of possible investment options. Moreover, all such proposals at the stage of their preliminary study are evaluated in comparison with the profitability of risk-free investments (bank deposit).
To understand the algorithm for calculating net present value, it should be taken into account that it is based on the methodology of discounting all available cash flows. That is why the decision to invest in a particular project is made after a preliminary calculation of the NPV of the project, within the framework of which:
- all expected inflows and outflows of capital for the accounting period are assessed;
- its value is determined (for the investor this value is considered as the discount rate);
- taking into account the mentioned rate, all incoming and outgoing flows are discounted;
- the results are summarized. The result obtained is the value of the present value of the project.
The resulting number can have the following values.
NPV = 0. This informs the investor that he has a probability of returning the invested funds with a minimal profit.
NPV< 0. Подобные инвестиционные проекты дальнейшему рассмотрению не подлежат.
NPV > 0. Investment should bring profit.
Basic calculation formula:
Symbols used:
- N is the number of periods (months, quarters, years) for which the project being evaluated is calculated;
- t is the time period for which the net present value is considered;
- i is the calculated discount rate for the investment option being evaluated;
- CF t – expected cash flow (net) for a specified time period.
An example of how NPV is calculated (for convenience, we summarize the results in tables and diagrams).
A comparative analysis of two projects with equal starting investments is performed. Let it be 5 million rubles. Both options are characterized by approximately equal risks of uncertainty of available cash flows. For simplicity of calculation, we will assume that the cost of raising funds is also the same and equal to 11.5%.
By filling out the form you agree to our privacy policy and consent to the newsletter
The main difference lies in the dynamics of inflows and outflows of funds.

Using the calculation formula given above, we obtain the following discounted flows

The obtained results of the NPV of the project should be interpreted as follows:
- if the investor is offered two independent projects, both should be accepted;
- if they are mutually exclusive, then project “A” has an undeniable advantage, since it has the best NPV.
The value of the discount rate when calculating NPV
When studying net present value, you should definitely pay serious attention to the indicator - the discount rate. It is often referred to differently as the opportunity cost of investment. The indicator used in the calculation formula denotes the minimum amount of profitability that the investor considers acceptable for risks comparable to those of the project being implemented.
An investor can operate with funds raised from various sources (own or borrowed).
1. In the first case, the discount rate set is a personal assessment of the acceptable risks of the investment project under consideration.
Its assessment can take several approaches. The simplest ones are:
- Selecting a risk-free rate, adjusted taking into account the likelihood of specific risks.
As such, the yield on securities of the state in which the project is being implemented and the rate of return on corporate bonds of companies in the industry are usually considered.
- Necessary and minimum sufficient (from the point of view of a potential investor) profitability (ROE indicator).
In this case, the person making the investment decision determines the discount rate according to one of the possible options:
- funds available on deposit in a specific bank are invested in the project. Therefore, the opportunity cost should not be less than the available bank rate;
- Funds withdrawn from business and temporarily available are invested in the project. If a need arises for them, prompt withdrawal of the entire amount from the project is impossible. A loan will be required. Therefore, the market lending rate is chosen as the current cost of funds;
- The average profitability of the main business is Y%. Accordingly, you are required to receive no less from an investment project.
2. When working with borrowed funds, the rate will be calculated as a derivative of the cost of funds attracted from various sources.
As a rule, the rate set by the investor in such cases exceeds a similar indicator of the cost of borrowed funds.
This not only takes into account changes in the value of funds over time, but also introduces possible risks associated with the uncertainty of cash flows and their volumes.
This is the main reason why the discount rate is considered to be the weighted average cost of capital attracted for subsequent investment (WACC).
It is this indicator that is considered as the required rate of return on funds invested in a specific investment project. The higher the expected risks, the higher the rate.
Calculation methods for determining this parameter are less clear than graphical ones. Especially when you need to compare the attractiveness of two or more projects.
For example, comparing projects “A” and “B” (see graph) the following conclusions can be drawn:

When the rate exceeds 7%, the NPV value of project A is higher than that of B (which warns of a possible error in the choice during arithmetic comparison).
In addition, investment project “B”, indicated on the red curve graph, is subject to more significant changes due to a changing discount rate (this can be explained by different amounts of incoming funds in the same period of time).
It is necessary to take into account the fact of a significant decrease in the value of discount rates over time, which imposes certain time restrictions. They can be calculated in no more than 10 years.
Analysis of the graphs allows us to conclude that a changing discount rate leads to changes in the value of the NPV indicator (and the latter changes nonlinearly).
Therefore, for a more balanced assessment, it is necessary not only to compare the values for different investment projects, but also to take into account changes in the latter at different rates.
By default, when calculating in Excel, the discount rate is assumed to be 10%.
Calculation of NPV using Excel
The program provides the ability to determine the value under consideration using the “NPV” function.

The operating algorithm is quite simple.
- select “H6” (output cell);
- after pressing fx (button) in the window that opens, first the category – “Financial”, and then the function – “NPV” is selected;
- going to the “Bet” field, select cell “C1”;
- then the range of data used (in this case it is C6:G6) is entered in a special field called “Value 1”. The second field should be left blank “Value 2”. After this, press “OK” (button).
Since the option under consideration does not take into account the initial (starting) investments in the project, you again need to enter “H6”, where you need to add an additional cell “B6” to the formula bar.

Pros and cons of the NPV calculation method
Among the advantages is the use of the so-called discounted cash flow technique. This provides the possibility of adequately assessing such a parameter as the amount of value additionally created as part of the implementation of the investment project.
But a number of serious shortcomings require their mandatory consideration.
These include the following:
- high sensitivity to ongoing changes in discount rates;
- ignoring cash flows, the receipt of which begins after the established deadline for the project.
Join over 3 thousand of our subscribers. Once a month we will send to your email a digest of the best materials published on our website, LinkedIn and Facebook pages.
Let's calculateReduced (to the current moment) costinvestments with different methods of calculating interest: using the simple interest formula, compound interest, annuity and in the case of payments of an arbitrary amount.
Present Value is calculated based on the concept of time value of money: money available now is worth more than the same amount in the future due to its potential to provide income. The calculation of the Present Value is also important, since payments made at different points in time can be compared only after bringing them to one point in time.
The current value is obtained as a result of reducing Future income and expenses to the initial period of time and depends on the method by which interest is calculated: , or (the example file contains a solution to the problem for each method).
Simple interest
The essence of the simple interest method is that interest is accrued throughout the entire investment period on the same amount (interest accrued for previous periods is not capitalized, i.e. interest is not accrued on them in subsequent periods).
In MS EXCEL, the abbreviation PS is used to denote Present Value (PV appears as an argument in numerous financial functions of MS EXCEL).
Note. MS EXCEL does not have a separate function for calculating Present Value using the Simple Interest method. The PS() function is used for calculations in the case of compound interest and annuity. Although, by specifying the value 1 as the Nper argument, and specifying i*n as the rate, you can force PS() to calculate the Present Value using the simple interest method (see example file).
To determine the Present Value when calculating simple interest, we use the formula for calculating (FV):
FV = PV * (1+i*n)
where PV is Present Value (the amount that is currently invested and on which interest is accrued);
i - interest rate during the period interest calculations (for example, if interest is accrued once a year, then annual; if interest is accrued monthly, then per month);
n is the number of time periods during which interest is accrued.
From this formula we get that:
PV = FV / (1+i*n)
Thus, the procedure for calculating Present Value is the opposite of calculating Future Value. In other words, with its help we can find out how much amount we need to invest today in order to receive a certain amount in the future.
For example, we want to know how much we need to open a deposit for today in order to accumulate 100,000 rubles in 3 years. Let the bank have a deposit rate of 15% per annum, and interest is accrued only on the principal amount of the deposit (simple interest).
In order to find the answer to this question, we need to calculate the present value of this future amount using the formula PV = FV / (1+i*n) = 100000 / (1+0.15*3) = 68,965.52 rubles. We received that today's (current, real) amount is 68,965.52 rubles. equivalent to the amount after 3 years in the amount of RUB 100,000.00. (at the current rate of 15% and calculated using the simple interest method).
Of course, the Present Value method does not take into account inflation, bank bankruptcy risks, etc. This method works effectively for comparing amounts “all other things being equal.” For example, that it can be used to answer the question “Which bank offer is more profitable to accept in order to receive the maximum amount in 3 years: open a deposit with simple interest at a rate of 15% or with compound interest with monthly capitalization at a rate of 12% per annum”? To answer this question, consider calculating Present Value when calculating compound interest.
Compound interest
When using compound interest rates, the interest money accrued after each compounding period is added to the amount owed. Thus, the basis for compounding, as opposed to using, changes in each compounding period. Adding accrued interest to the amount that served as the basis for its accrual is called capitalization of interest. This method is sometimes called "percentage on interest."
The present value of PV (or PS) in this case can be calculated using.
FV = РV*(1+i)^n
where FV (or S) is the future (or accumulated amount),
i - annual rate,
n is the loan term in years,
those. PV = FV / (1+i)^n
When capitalizing m times a year, the Present Value formula looks like this:
PV = FV / (1+i/m)^(n*m)
i/m is the rate for the period.
For example, the amount is 100,000 rubles. in the current account in 3 years is equivalent to today's amount of 69,892.49 rubles. at the current interest rate of 12% (% accrued monthly; no replenishment). The result was obtained by the formula =100000 / (1+12%/12)^(3*12) or by the formula =PS(12%/12;3*12;0;-100000).
Answering the question from the previous section “Which bank offer is more profitable to accept in order to receive the maximum amount in 3 years: open a deposit with simple interest at a rate of 15% or with compound interest with monthly capitalization at a rate of 12% per annum”? we need to compare two Present values: 69,892.49 rubles. (compound interest) and 68,965.52 rub. (simple interest). Because The present value calculated according to the bank’s offer for a deposit with simple interest is less, then this offer is more profitable (today you need to invest less money in order to receive the same amount of 100,000.00 rubles in 3 years)
Compound interest (multiple amounts)
Let us determine the present value of several amounts that belong to different periods. This can be done using the PS() function or the alternative formula PV = FV / (1+i)^n
By setting the discount rate to 0%, we simply obtain the sum of the cash flows (see example file).
Annuity
If, in addition to the initial investment, additional equal payments (additional investments) are made after equal periods of time, then the calculation of the Present Value becomes significantly more complicated (see the article, which shows the calculation using the PS() function, as well as the derivation of an alternative formula).
Here we will analyze another task (see example file):
The client opened a deposit for a period of 1 year at a rate of 12% per annum with monthly interest accrual at the end of the month. The client also makes additional contributions in the amount of 20,000 rubles at the end of each month. The value of the deposit at the end of the term reached 1,000,000 rubles. What is the initial deposit amount?
The solution can be found using the PS() function: =PS(12%/12;12;20000;-1000000;0)= 662,347.68 rub.
Argument Bid indicated for the period of accrual of interest (and, accordingly, additional contributions), i.e. per month.
Argument Nper– is the number of periods, i.e. 12 (months), because the client opened a deposit for 1 year.
Argument Plt- this is 20,000 rubles, i.e. the amount of additional contributions.
Argument Bs- this is -1000000 rub., i.e. future value of the deposit.
The minus sign indicates the direction of cash flows: additional contributions and the initial deposit amount are of the same sign, because client lists these funds to the bank, and the future amount of the client’s deposit will receive from the bank. This very important note applies to everyone, because... otherwise, you may get an incorrect result.
The result of the PS() function is the initial deposit amount, it does not include the Present value of all additional contributions of 20,000 rubles. This can be verified by calculating the present value of additional contributions. There were 12 additional contributions in total, the total amount was 20,000 rubles * 12 = 240,000 rubles. It is clear that at the current rate of 12%, their present value will be less = PS(12%/12;12;20000) = -225,101.55 rub. (up to sign). Because these 12 payments made over different periods of time are equivalent to RUB 225,101.55. at the time of opening the deposit, they can be added to the initial deposit amount calculated by us, 662,347.68 rubles. and calculate their total Future Value = BS(12%/12;12;; 225,101.55+662,347.68)= -1000000.0 rub., which was what needed to be proven.
When considering various investment projects, there is a need for an objective assessment of their effectiveness. Calculation of the net present value indicator (NPV, NPV - “net present value” - English) helps to cope with this task.
This is the sum of the differences between expected cash receipts and project costs, discounted at a given interest rate. Thus, NPV shows the value of future cash flows, reduced to today, which allows you to objectively assess the profitability of the investment plan.
The calculation of the indicator must be performed in stages:
- Find the difference between projected profit and investment costs for each period of time (usually a year).
- Determine the discount rate by determining the cost of capital.
- Bring the results obtained to today - discount cash flows separately for each period.
- Find the sum of all discounted cash flows (both negative and positive). This value will constitute the NPV, which shows the investor’s total profit.
Necessity of calculation
 Calculating net present value is one of the most popular methods for predicting the effectiveness of investment programs. Assessing the value of this indicator allows us to answer the main question for an entrepreneur: “Should I invest money in the project or not?”
Calculating net present value is one of the most popular methods for predicting the effectiveness of investment programs. Assessing the value of this indicator allows us to answer the main question for an entrepreneur: “Should I invest money in the project or not?”
The need to determine NPV is due to the fact that the coefficient allows not only to estimate the amount of predicted profit, but also to take into account the fact that any amount of money at the current time has a greater real value than the same amount in the future.
So, for example, instead of investing in a project, an entrepreneur can:
- Open a deposit account in a bank and receive an annual profit in accordance with the interest rate.
- Purchase property whose value will increase in the future by the amount of inflation.
- Hide money.
Therefore, the indicator is calculated using a given discount percentage rate, which allows take into account inflation and risk factors, as well as evaluate the effectiveness of the project in comparison with alternative investment options.
Formula and calculation examples
The formula for calculating NPV is as follows:
- t, N – number of years or other time periods;
- CF t – cash flow for period t;
- IC – initial investment;
- i – discount rate.
In order to correctly understand the methodology for calculating this indicator, let’s consider it using a practical example.
Let's say an investor is considering the possibility of implementing two projects - A and B. The program implementation period is 4 years. Both options require an initial investment of RUB 10,000. However, the projected cash flows of the projects differ greatly and are presented in the table:
| Year | Cash flows of project A, rub. | Cash flows of project B, rub. |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | -10000 | -10000 |
| 1 | 5000 | 1000 |
| 2 | 4000 | 3000 |
| 3 | 3000 | 4000 |
| 4 | 1000 | 6000 |
Thus, project A assumes maximum profit in the short term, and project B implies its gradual increase.
Let's determine the NPV of projects at a given discount rate of 10%:

Due to the fact that discount factors become smaller with each subsequent year, the contribution of larger, but more distant cash flows to the total net present value decreases. Therefore, the NPV of project B is less than the corresponding value of project A.
The step-by-step calculation process is discussed in detail in the following video:
Analysis of the result
The main rule that is relied upon when assessing the effectiveness of investments using the NPV method is the project should be accepted if the indicator value is positive. If this value is negative, then the investment plan is unprofitable.
If the indicator turns out to be 0, it is necessary to understand that the income cash flows from the implementation of the program are capable of reimbursing the costs, but nothing more.
Let's go back to the example above. The NPV of both projects turned out to be positive, which suggests that the investor can invest in any of them, because they are capable of generating profit. However, the NPV for project A exceeds the same value for project B, which indicates its greater efficiency. It is investing in the first project that is most profitable for an entrepreneur - after 4 years of implementation with an initial cost of 10,000 rubles. it is able to bring a net profit of 788.2 rubles.
Thus, it is worth remembering: the higher the NPV of an investment, the higher its efficiency and profitability. 
Advantages and disadvantages of the method
Despite the advantages of the method, such as taking into account changes in the value of funds over time and taking into account risks, you should remember a number of limitations:
- All indicators used in the calculations are predictive in nature and remain stable throughout the entire duration of the program. In reality, they can vary significantly from the given values, which makes the final value only a probabilistic parameter.
- Discount rates are often adjusted taking into account possible risks, which is not always justified and leads to an unreasonable decrease in the final NPV value. In this regard, the investor may refuse to implement a profitable project.
Thus, the NPV calculation method makes it possible to easily and qualitatively assess the likely profitability of investments given to the current point in time.
However, it is worth remembering that this technique is predictive in nature and is only suitable in a stable economic situation.