Slow growth of hcg in the early stages. Why is hcg rising slowly. Are incorrect results possible?
Why is hCG rising slowly? This is a frequently asked question among women who are preparing to become mothers for the first time. Human chorionic gonadotropin, or hCG, is a hormone produced by the embryonic organ of a woman during the period of bearing a child, it is one of the leading indicators of its presence and successful flow. Up to 7-11 weeks, its growth occurs rapidly, then slows down. In the first 3 months, chorionic gonadotropin causes the production of progesterone and estrogen - hormones necessary for the successful development of pregnancy.
Hormones are chemicals produced by special cells in the glands and other organs of the body; most hormones are produced by cells in the endocrine glands. These hormones, which are produced in very small amounts, are released into the bloodstream and sent to the "target organ" or tissue where they have their effect.
Several hormones are involved in growth regulation. Some act directly on target organs, while others act by causing the production of other hormones that activate certain organ functions needed for growth. This finely tuned system may not work correctly, resulting in abnormal growth.
Establishing the level of gonadotropin during pregnancy
An analysis of the degree of content of chorionic gonadotropin allows you to establish the presence of pregnancy at a time when an ultrasound examination cannot yet give results. Stimulation of the production of progesterone and estrogen by chorionic gonadotropin continues until the woman's embryonic organ (placenta) begins to produce and form hormonal background on one's own. HCG is made up of an alpha unit and a beta unit. Of these, the beta unit is unique in its composition, which makes it possible to use it in tests to determine pregnancy. An analysis of the amount of beta-gonadotropin in the blood makes it possible to determine the presence of pregnancy after 14 days.
Establishing the level of gonadotropin during pregnancy
The pituitary gland is often referred to as the master gland because it produces several hormones that control the functions of other glands. It is located in the middle of the skull below the part of the brain called the hypothalamus. The pituitary gland has two separate parts: the anterior lobe and the posterior lobe. The pituitary gland releases its hormones in response to chemical messages from the hypothalamus, the part of the brain to which it is connected.
Growth hormone is an anterior pituitary hormone whose main effect is to stimulate the growth of body tissues. Other anterior pituitary hormones affect growth indirectly by working through other glands. Thyroid stimulating hormone - causes the thyroid gland to produce thyroid hormone, which regulates the body's metabolism and is essential for normal growth. Adrenocorticotropic hormone - causes the adrenal glands to produce cortisol and other hormones that allow the body to respond to stress. Luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone - cause the gonads to produce sex hormones that are necessary for adolescent sexual development and growth that accompanies puberty. Too much cortisol will cause a growth retardation in a child. . The main hormone produced by the posterior pituitary is called vasopressin or anti-diuretic hormone.
A drop in the amount of chorionic gonadotropin in the blood during pregnancy or a decrease in its growth rate indicate a spontaneous miscarriage or the development of a fetus outside the uterus.
The presence of elevated levels of gonadotropin in men, as well as non-pregnant women, serves alarm signal. At best, this is an incorrectly performed analysis, at worst, the beginning of the development of oncological tumors in the body.
It controls the exit of water through the kidneys. Growth hormone deficiency can occur on its own or in combination with one or more pituitary hormone deficiencies. It may be complete or partial. Hypopituitarism can be congenital, resulting from abnormal formation of the pituitary or hypothalamus prior to birth, or from child acquisition caused by damage to the pituitary or hypothalamus during or after birth. Congenital hypopituitarism is present at birth, although it may not become apparent for many months.
Acquired hypopituitarism can present any time during infancy or childhood and may occur after severe traumatic brain injury or serious illness such as meningitis or encephalitis. Many cases of acquired hypopituitarism are the result of a tumor called a craniopharyngioma. This tumor can press on the hypothalamus or pituitary gland, causing one or more hormonal deficiencies. Deficiency consists of surgical removal of the tumor, which usually results in permanent hypopituitarism.
Tests for hCG hormone
To determine the presence of the hormone chorionic gonadotropin in the blood, a woman needs to pass urine and blood for analysis. The analysis is done in morning hours and on an empty stomach. When scheduling an analysis for another time, it must be remembered that at least 5 hours must pass between the meal and the procedure.
 In terms of reliability, a blood test comes first, the most inaccurate method is a pregnancy test, although it is popular among women. Why is a hormone analysis prescribed? Gynecologists do this in order to:
In terms of reliability, a blood test comes first, the most inaccurate method is a pregnancy test, although it is popular among women. Why is a hormone analysis prescribed? Gynecologists do this in order to:
Are incorrect results possible?
Sometimes there is no reason for hypopituitarism, or if a cause is suspected, it can be difficult to prove. Researchers are trying to learn more about the causes of growth hormone deficiency and hypopituitarism. A child with growth hormone deficiency is often small, with an immature face and a plump body. The growth rate of all parts of the body is slow, so that the proportions of the child remain normal. If a child's height has been plotted on a growth chart, it will likely level off and deviate from the child's established growth curve.
- diagnose early pregnancy;
- monitor the development of pregnancy;
- exclude the development of the fetus outside the uterus;
- identify pathologies in the development of the child;
- detect fetal fading in time;
- establish the risk of miscarriage;
- diagnose malignant tumors.
For the diagnosis of testicular tumors, such an analysis is also prescribed for men.
If there is a growth failure for a long time, the child may be much shorter than other children of the same age. This is why height and weight measurements plotted on a growth chart are so important - the earlier a problem with treatable growth is identified, the better the child's chance of maintaining a normal height throughout childhood and realizing his or her full growth potential.
Any child who is only as tall as children two or more years younger or who deviates from a previously normal growth curve should be evaluated by a physician. Pediatric endocrinologists are doctors who specialize in treating children with growth and hormonal problems. Depending on the situation, the doctor may measure the child over a period of six to twelve months to accurately determine the child's growth rate.
Often a gynecologist asks to do a second blood test with an interval of one week in the same laboratory. This is done to accurately establish pregnancy or eliminate errors in the analysis. With an increase in the level of gonadotropin in 1.5-2 times you can say that the woman is pregnant. If its level has not increased or decreased, then there is no pregnancy. You need to know that the norms and accuracy of determining the level of human chorionic gonadotropin are different in all laboratories.
The assessment begins with collecting information about the height of relatives and the presence of any health problems in the family. A history of early or late puberty in family members should be mentioned. The doctor will want to know about the mother's pregnancy, labor, and delivery. All measurements of the child's height and weight from birth should be collected so that the doctor can plot them on a growth chart. The doctor will ask questions about the general health and conditions of the child, past illnesses, injuries and stress.
A thorough physical examination will be done and x-rays of the hand and wrist can be taken to see how bone development compares with height and chronological age. A small amount of blood may be drawn to look for evidence of thyroid hormone deficiency and kidney, bone, and gastrointestinal disease.
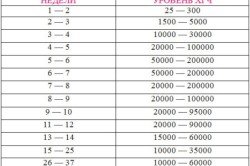 For men, as well as women who are not in a position, the content of gonadotropin is in the range from 0 to 5 mU / ml (international units per 1 ml).
For men, as well as women who are not in a position, the content of gonadotropin is in the range from 0 to 5 mU / ml (international units per 1 ml).
In the normal course of pregnancy, the content of gonadotropin is directly dependent on its duration, from conception to recent weeks term, it increases from 25 mU / ml to 78000 mU / ml. During the first trimester, the level of hCG increases several thousand times, then the sharp increase in the number of hormones stops and occurs slowly. The change in the level of gonadotropin is purely individual for each woman, there are no rigid limits. During the period of bearing a baby, there is an increase or decrease hCG levels.
This simple evaluation often gives the doctor enough information to determine the cause of a growth problem or to decide that a growth problem does not exist. If the doctor suspects that there is a problem with the pituitary gland, further testing is needed. A series of blood tests can measure hormone concentrations in the blood and the ability of the pituitary gland to respond to various stimuli. These tests may be done in a clinic or during a brief hospital stay.
Tests for hCG hormone
Growth hormone deficiency is moderately difficult to diagnose because the pituitary gland produces growth hormone in bursts. This means that the level of growth hormone in one random blood sample is likely to be very low. One way to test for growth hormone deficiency is to give the child a substance that causes the release of growth hormone in normal children and measure the amount of growth hormone present in several blood samples taken over a period of time. Because any child cannot respond to any given test on a given day, more than one stimulus may be needed to evaluate a child's ability to produce growth hormone.
The content of gonadotropin in the blood increases too quickly in case of:
- incorrect determination of the term (the term is longer than expected);
- multiple pregnancy;
- cystic drift.
 HCG rises too slowly if:
HCG rises too slowly if:
Several growth hormone stimulants have been identified. These include vigorous exercise and several chemicals and drugs. Another way to test growth hormone secretion is to hospitalize the child and measure the amount of growth hormone present in blood samples obtained overnight while sleeping or even during the entire 24-hour period. Because about two-thirds of total growth hormone production occurs during deep sleep, this test provides a better indication of how much growth hormone a child's pituitary gland normally produces.
- there was an error in determining the deadline (the deadline is less than expected);
- delay in fetal development;
- the fetus develops outside the uterus;
- fetal fading occurred;
- there is a risk of miscarriage.
Are incorrect results possible?
The possibility of obtaining incorrect results in a blood test for chorionic gonadotropin is not excluded. Such conclusions are called false positive or false negative.
If several tests show that growth hormone is not present, or that the amount of growth hormone produced is insufficient to support normal growth, a diagnosis of growth hormone deficiency is made. Much work is being done to develop more accurate and reliable methods for diagnosing growth hormone deficiency. Even the definition of growth hormone deficiency is being revised as researchers learn more about the conditions that can cause incomplete growth hormone deficiency.
Growth hormone deficiency is treated with growth hormone injections. This fast-than-normal growth rate slowly declines over time, but it will still be greater than without treatment. Many parents report an increase in their child's appetite and fat loss after starting treatment.
The first case in which there is no pregnancy, but the result is positive, is very rare.
Wrong negative result(the analysis does not confirm the presence of a pregnancy) is possible in case of violation of the rules when donating blood, with an incorrect determination of the gestational age, with late ovulation and in exceptional circumstances - ectopic pregnancy.
Treatment for growth hormone deficiency is usually given over several years until the child reaches an acceptable adult height or reaches maximum growth potential. As with other conditions, children and parents may be impatient to see faster or more impressive results from therapy. They may become discouraged even if treatment is on according to plan. It is important to remember that growth is a slow process that is measured over several months; Children who expect to grow overnight when they start Deficiency will be disappointed.
If you suspect an erroneous result in both cases, the gynecologist recommends taking the tests again.
In addition, the content of gonadotropin in the blood is affected by drugs used to treat infertility and containing this hormone (Horagon, Pregnil). Before testing, it is necessary to warn laboratory workers about taking such drugs. Other drugs do not affect the level of hCG in the blood.
Changes in hCG levels during pathological pregnancy
Your child's doctor will discuss realistic short-term and long-term expectations for therapy with you. If testing reveals other hormone deficiencies, medications are available to replace them; thyroid hormone, cortisol, and sex hormones can be easily administered if they are lacking. It is important that these hormones are taken as directed because normal growth can only occur when all hormones are present in the proper amounts. good food and adequate rest are important for normal growth in all children.
Changes in hCG levels during pathological pregnancy
An increase in the amount of gonadotropin in the blood during an ectopic pregnancy is not as stable as in a normal one. In the first week, while the egg develops outside the uterus (ovary or fallopian tube), its level rises. But already from the second month there is a decrease in the amount of the hormone. Comparing the test results with the norm, it is possible to diagnose the pathological nature of pregnancy. Typically, deviations from normal indicators noticeable already from the middle of the third month.
Until recently, the only source of human growth hormone was the pituitary glands of deceased people obtained at autopsy. Since this type of growth hormone does not come from humans, it is unlikely that human diseases can be transmitted through it.
Biosynthetic growth hormone is supplied as a powder in sterile vials. Parents and children are taught how to mix the powder with the solution and inject. Treatment is continued for as long as growth potential exists and the child responds to therapy. With early diagnosis and a good response to treatment, children with growth hormone deficiency can expect to achieve normal adult height.
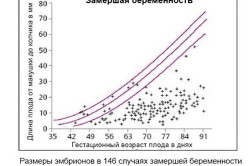 There are cases when the fetus stops its development in the uterus and dies. This is a frozen pregnancy. At a very early stage, the heartbeat is not yet audible and is not determined by ultrasound. It is possible to identify pathology only by the level of gonadotropin in the blood. In most cases, fading occurs in the first 3 months. With a frozen pregnancy, the growth of the uterus continues, but the level of gonadotropin does not increase, but gradually decreases.
There are cases when the fetus stops its development in the uterus and dies. This is a frozen pregnancy. At a very early stage, the heartbeat is not yet audible and is not determined by ultrasound. It is possible to identify pathology only by the level of gonadotropin in the blood. In most cases, fading occurs in the first 3 months. With a frozen pregnancy, the growth of the uterus continues, but the level of gonadotropin does not increase, but gradually decreases.
Children who are short of their age sometimes have problems because students and teachers treat them like they are younger, not younger. Parents tend to do this too, and lower their expectations of the child. These children then cannot fulfill their age because they are not expected to. Framing and calling out a name can be hard. Some of these problems can be helped by frank and open discussion with teachers and classmates.
For more information about psychosocial adaptation to short stature, ask parents of short children and your growth clinic doctor, nurse, and psychologist. Biosynthetic Growth Hormone is available in unlimited quantities for Deficiency in all children with growth hormone deficiency. It is possible that growth hormone substitutes may become available as research continues.
Pathologies also include pregnancy with two or more fetuses. The reason for this phenomenon may be:
- heredity (there was a similar case in the family of one of the parents);
- maturation of several follicles or one, but containing several eggs;
- taking hormonal drugs;
- conception at a late age;
- in vitro fertilization.
The level of gonadotropin when carrying two or more embryos is necessarily higher than during a normally developing pregnancy with one fetus.
Typically, hCG levels for multiple pregnancies are at least 2 times higher than the content of chorionic gonadotropin in a singleton.
Age-related changes in the body of a woman, due to the cessation menstrual cycle, also lead to a slow increase in chorionic gonadotropin in the blood. For women during menopause, a level of 14 mU / ml is considered the norm.
After an abortion or loss of a child as a result of a miscarriage, the level of gonadotropin remains slightly above normal for several days. After 1.5 months it's getting closer to normal.
Hello Elena Viktorovna! I have a difficult situation. There was endometrial polypropylene, successfully removed and took duphaston for more than 6 months, the long-awaited delay has come. The last menstruation was 08/29/2016, 10/17/2016 passed hCG, the doctor said the result was negative and the tests did not show all this time and did not show after. I was referred to a family planning center. On 10/28/2016 I was at a reception at this center, during the examination they immediately did a transvaginal ultrasound and the doctor said don’t worry, menstruation will come now. On this day, a rash had already begun on the forehead and mainly in the temporal part of the forehead - transparent watery pimples in a large amount, and after each meal I felt very sick, but without vomiting, I already lost two kilos in ten days, then the nausea went away, and with her, the appearance of acne disappeared. But now, a week after the visit to the family planning center, there are no periods and no, I decide to drink duphaston, because before that the attending physician said that when you get pregnant, you will take it continuously for several months. The second week has passed since the last examination, and on November 11 and 12 he begins to smear, the discharge is brown, pain minor on the lower right. On Sunday the 13th, blood bleeds like during menstruation, but only in a smaller number of times twice (but in general I have abundant and the cycle has leveled off with difaston up to 28 days, and the duration of the days themselves is 4) the next day the bleeding decreases and seems to stop , to which I sigh with relief and pray to God that everything works out and the pregnancy is preserved. 14 in the morning I see that they were at night brown discharge, I try not to heat up, I go to work. And already at work, the following also happens in the morning: I feel a splash and a splash of fluid from me - blood, I put on a gasket, I am in shock, I try not to hysteria, and within 2-3 hours, bleeding and pieces up to 4 cm in size by 1.5-2 cm , so there were about 5-6 pieces during this time and the bleeding subsided by the evening, today we can already say it doesn’t drip, but the sensations both yesterday and today in the lower abdomen are as if the muscles were in good shape after training, although there were no physical loads at all. Tomorrow I have a scheduled appointment with my doctor, as the family planning center has scheduled a lot of tests for both hormones and smears. Why didn’t I immediately run to the doctor, but would they accept me, because the pregnancy was not diagnosed? Yes, and I began to come to myself only today, before that I didn’t think anything. Q: Was you pregnant? What happened is a miscarriage? And for what reasons could not establish whether there is a pregnancy or not? Thank you for your attention and looking forward to your answer, I want to clarify the situation for myself and see what my doctor can tell me.




